Connection Profile Module
1. Introduction
The Connection Profile Management module is the bridge between DataFuse AI and your external data. Before you can run queries, build pipelines, or analyze information, the system needs to know where your data lives and how to access it safely. A Connection Profile saves these details—like the address of your database and your login credentials—so you don't have to enter them every time.
Why is it Important?
- Centralized Access: Manage all your data sources (SQL, NoSQL, Cloud Storage) in one dashboard.
- Security: Your credentials (usernames and passwords) are saved securely.
- Efficiency: Create a profile once and reuse it across multiple Pipelines and Queries.
Key Benefits
- Plug-and-Play: Supports a wide variety of sources including PostgreSQL, MySQL, S3, Snowflake, and MongoDB.
- Safety First: Includes features to test connections before saving to prevent errors.
- Visual Status: Instantly see if a connection is healthy (Green) or broken (Red).
Use Case Example
Imagine you are a Data Analyst. You have sales data stored in a PostgreSQL database and customer logs in an Amazon S3 bucket. You can create two separate Connection Profiles in DataFuse AI. Once created, you can effortlessly drag and drop these data sources into a Pipeline to merge the data, without ever looking up the IP addresses or passwords again.
2. How to Use the Connection Profile Management
Step-by-Step Instructions for Creating, Editing, and Managing Connection Profiles
-
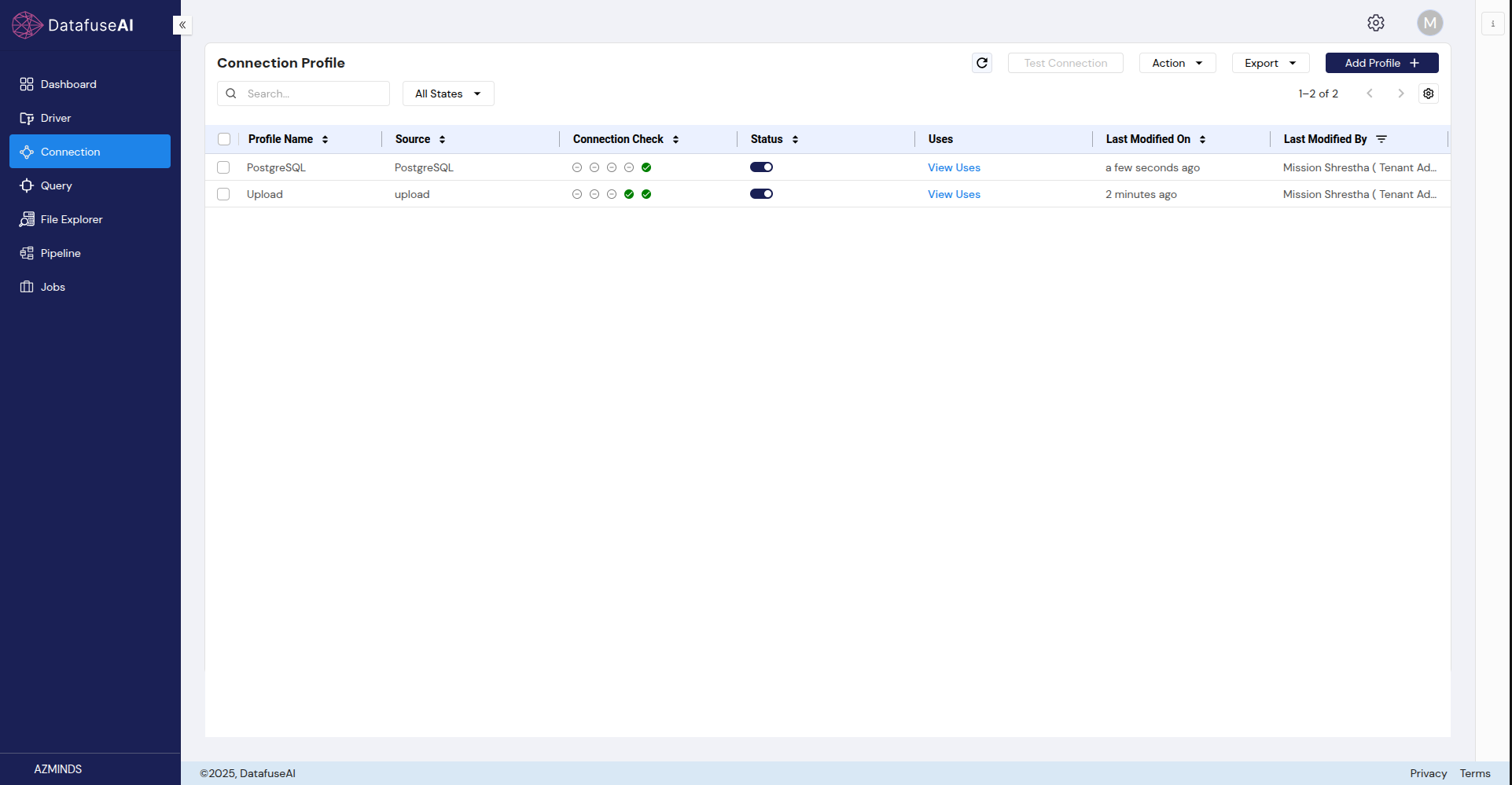
Viewing Existing Connection Profiles
- Log in to DataFuse AI and navigate to the Connection tab.
- The Connection Profile page will display a list of all profiles, including details such as profile name, source, connection status, and more.
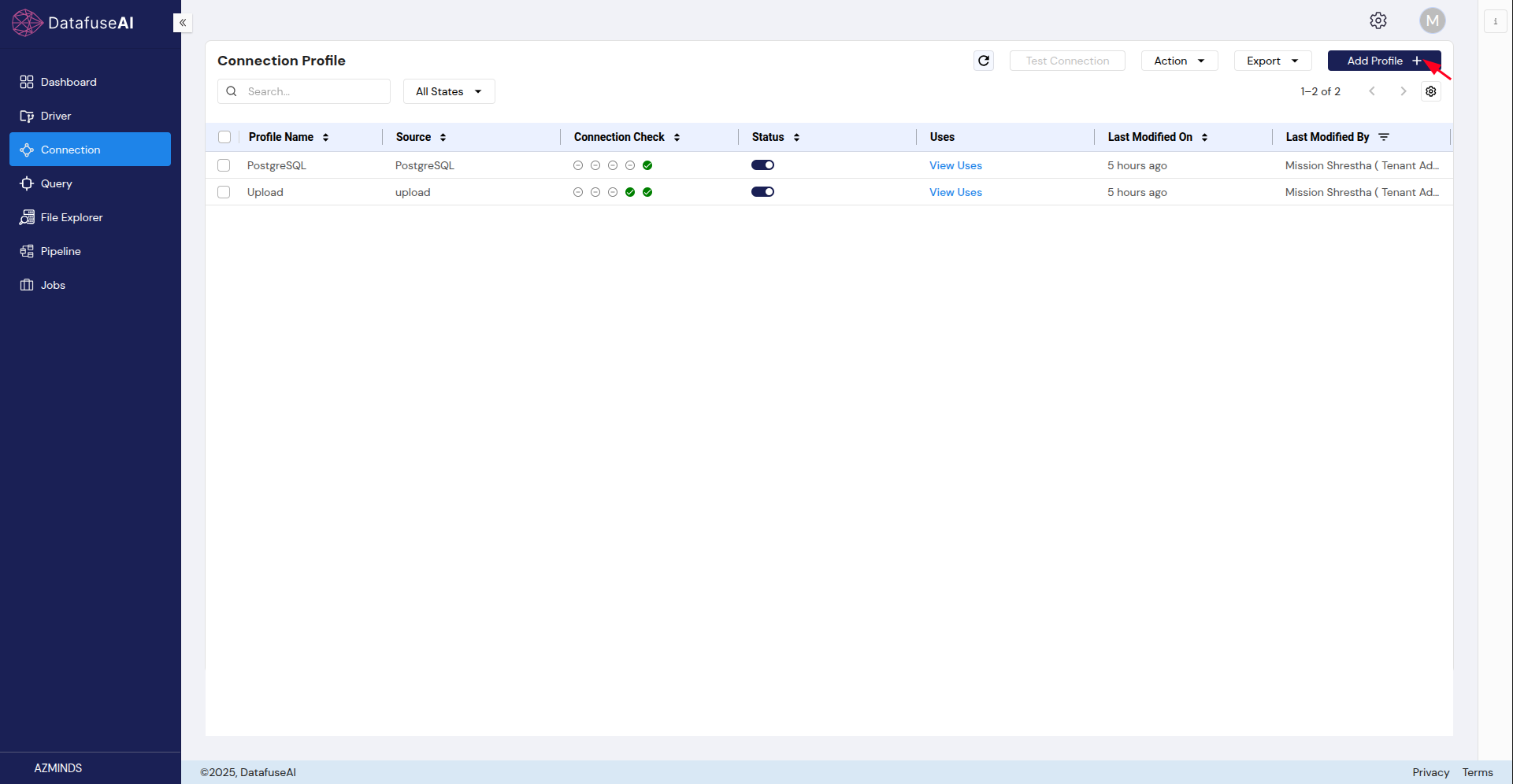
 2. Creating a New Connection Profile
2. Creating a New Connection Profile
-
Click the Add Profile button at the top-right corner of the profile list.
-
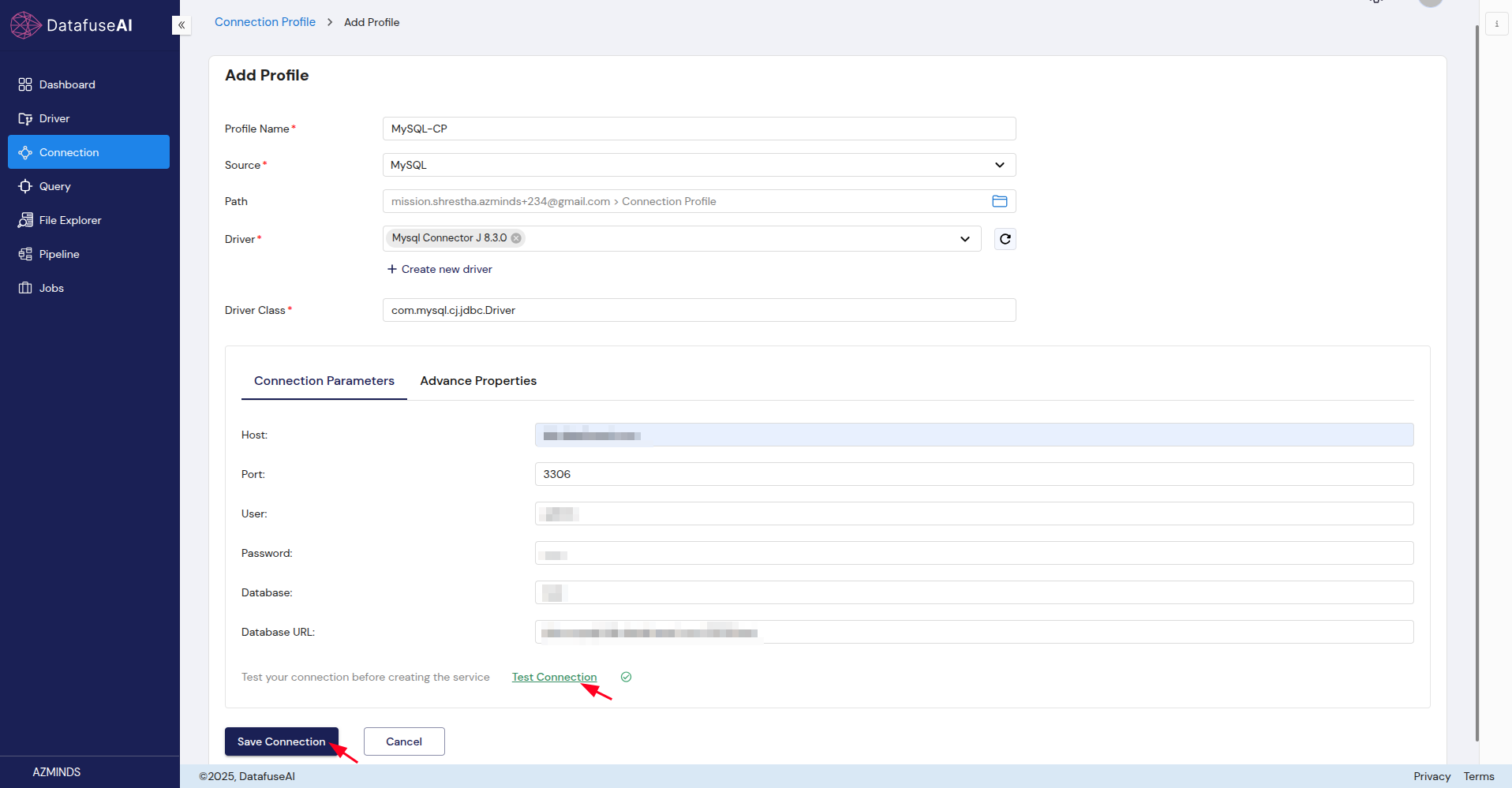
Complete the form:
- Profile Name: Choose a name for the connection.
- Source: Select the data source type (e.g., PostgreSQL, MySQL).
- Driver: Select the appropriate driver for the data source.
- Connection Parameters: Enter details such as host, port, username, password, and database name.(specifics vary by data source; see Section 9 for details).
-
Click Save Connection to create the new profile.
 3. Editing an Existing Profile
3. Editing an Existing Profile
- Click the Edit button in the Actions dropdown menu next to the profile.
- Modify the profile details as needed (e.g., profile name, connection parameters).
- Click Save Connection to apply the changes.
-
Testing a Connection
- Select the profile you wish to test.
- Click the Test Connection button to verify if the connection to the data source is successful.
- A color-coded indicator will show the connection status (green for success, red for failure).
-
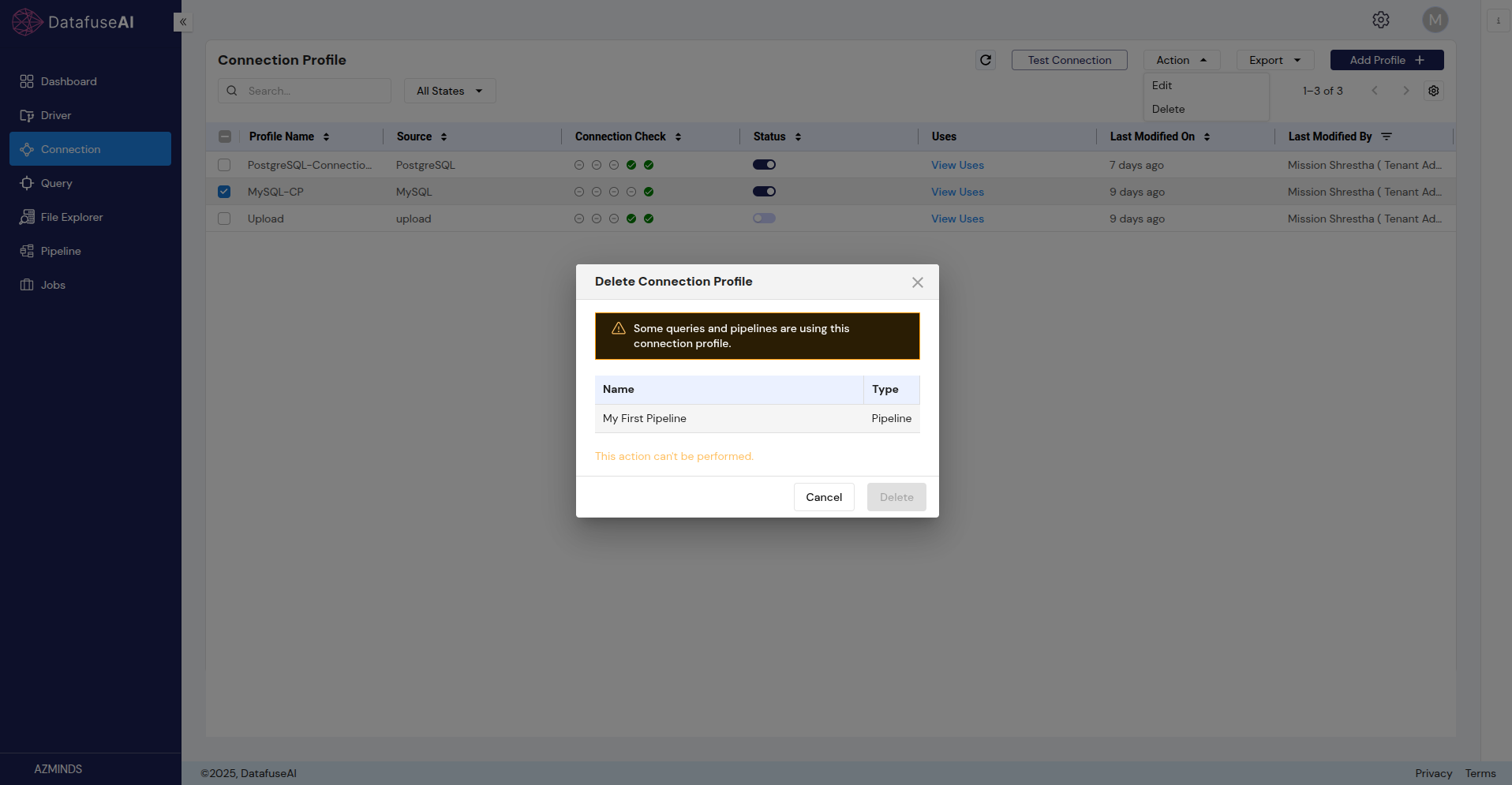
Deleting a Profile
- Click the Delete option in the Actions dropdown menu.
- A confirmation prompt will appear if the profile is in use (e.g., in queries or pipelines). If it is not in use, the profile will be deleted immediately.
Real-Life Scenario: Connecting to a PostgreSQL Database
Goal: connect to the Finance Department's server.
- Click Add Profile.
- Name: Finance_Postgres_Main
- Source: Select PostgreSQL.
- Host: Enter 192.168.1.50 (The IP address provided by your IT team).
- Port: Enter 5432 (The default for PostgreSQL).
- User/Password: Enter your credentials.
- Database: Enter finance_db.
- Click Test Connection. The indicator turns Green.
- Click Save Connection.
3. Configuration Reference by Data Source
This section details the configuration options available when setting up Connection Profiles for various data sources in DataFuse AI. The configuration settings differ depending on whether you're connecting to relational databases, NoSQL databases, cloud storage systems, or cloud-based databases like RDS.
Advanced Properties (Common for All Sources)
These are global settings that apply to all types of connections, allowing you to fine-tune your connections to suit specific requirements.
- Preview Limit: Set to 10. This option controls the number of records that will be previewed when testing the connection. The default value is 10, but it can be adjusted to load more or fewer records.
- Packet Size: Set to 10. This determines the size of each packet of data being transferred between DataFuse AI and the data source. Larger packet sizes may improve performance for large datasets, but smaller packets could prevent memory overload.
- Number of Partitions: This field allows users to configure the number of partitions during the data transfer process. Adjusting this setting can optimize data handling by splitting the data into multiple parts, though it is not currently visible in all user interfaces.
- Connection Timeout: Set to 0. This configuration specifies the amount of time (in seconds) that DataFuse AI will wait before timing out the connection attempt. A value of 0 means that no timeout is applied.
- SSL: This toggle allows you to enable or disable SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) for securing your connection. By default, SSL is disabled, but it can be turned on for encrypted communication with supported data sources.
- Encrypt: This toggle enables or disables data encryption for the connection. Encryption ensures that the data being transferred remains private. By default, encryption is disabled, but it can be enabled when needed.
1. Relational Databases (RDBMS)
DataFuse AI supports multiple relational database management systems (RDBMS), allowing seamless integration with various SQL databases. Below are the configuration details for some of the most common relational databases.
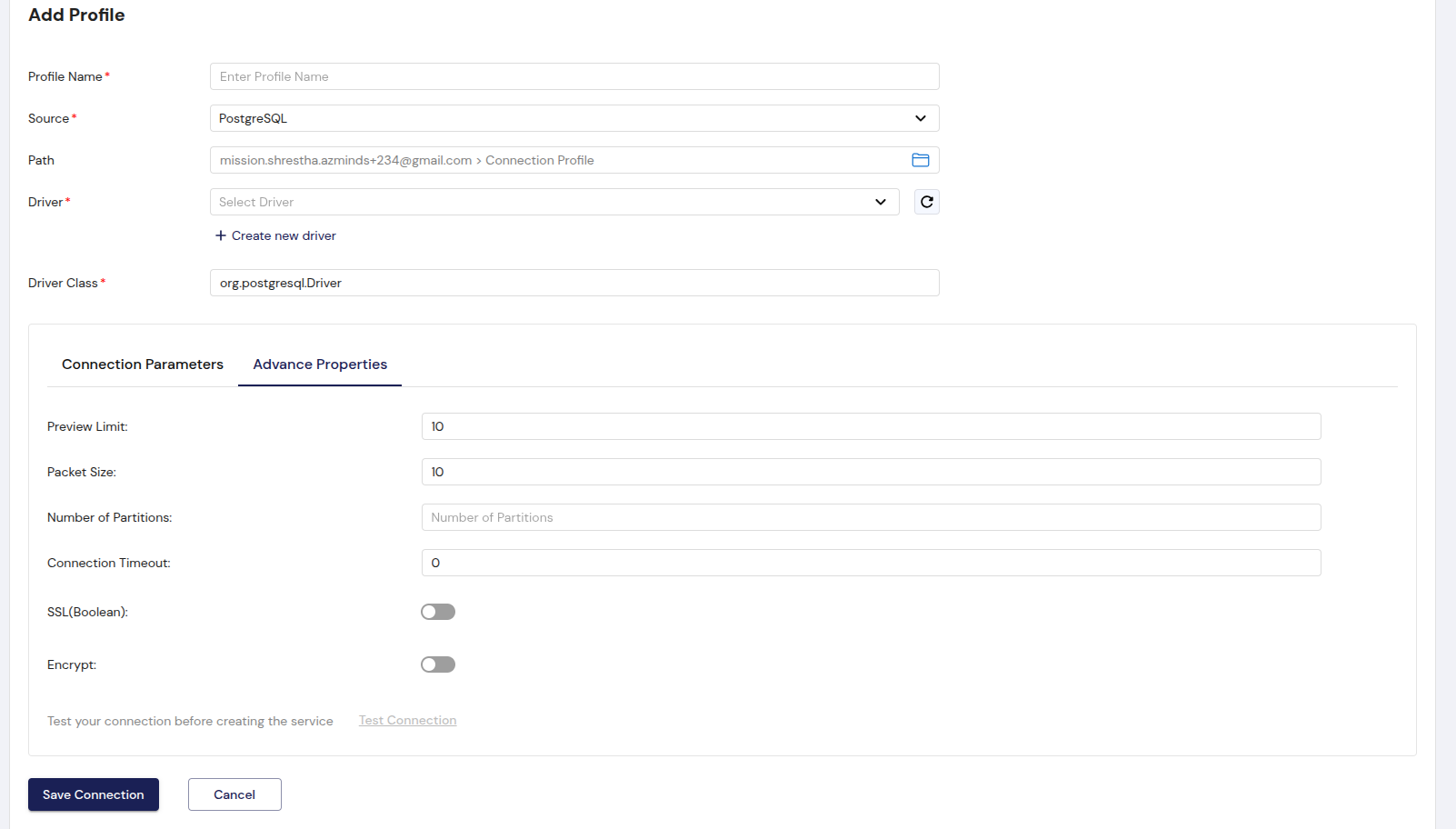
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is a popular open-source relational database known for its robust features and SQL compliance.
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: Enter a name for your PostgreSQL connection profile.
- Source: Select PostgreSQL from the dropdown list.
- Path: Displays the current path for the PostgreSQL connection, automatically populated once the profile is created.
- Driver: Select Postgresql 427.3 from the driver options.
- Driver Class: org.postgresql.Driver, the driver used for PostgreSQL connections.
Connection Parameters:
- Host: The domain name or IP address of the PostgreSQL server.
- Port: The port number to use for the PostgreSQL connection (default is 5432).
- User: The username for authenticating the PostgreSQL connection.
- Password: The password associated with the PostgreSQL username.
- Database: The name of the PostgreSQL database to connect to.
- Database URL: The JDBC URL for connecting to the database, which follows the pattern: jdbc:postgresql://[host]:[port]/[database].
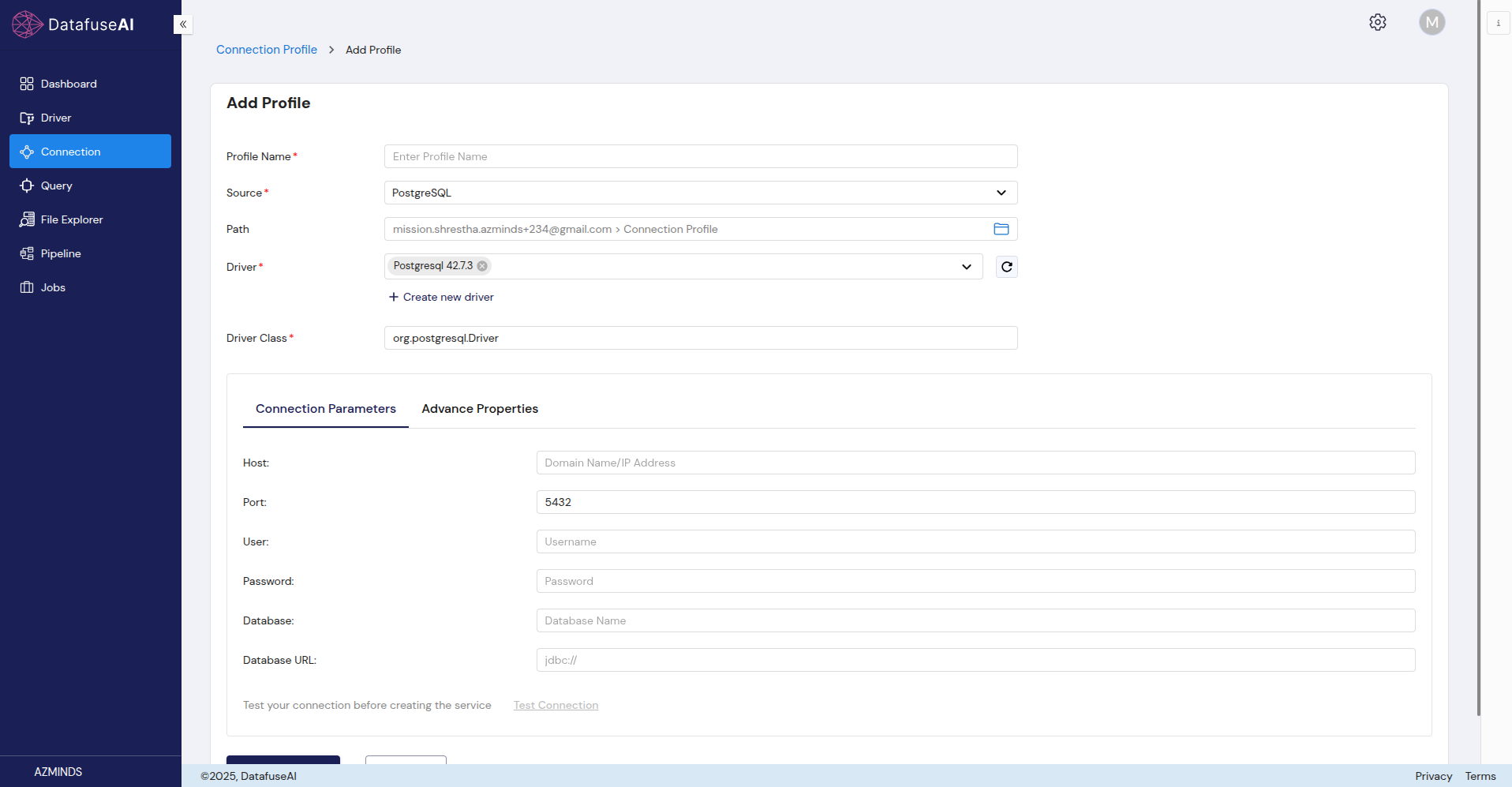
MSSQL (Microsoft SQL Server)
MSSQL is a relational database management system developed by Microsoft.
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: Choose a descriptive name for the MSSQL connection.
- Source: Select MSSQL from the dropdown.
- Path: The path to the MSSQL profile.
- Driver: Select Mssql Jdbc 12.6.1 jre11 from the available drivers.
- Driver Class: com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver, the driver used for MSSQL connections.
Connection Parameters:
- Host: The IP address or domain name of the MSSQL server.
- Port: The connection port (1433 is the default for MSSQL).
- User: Username for MSSQL authentication.
- Password: Password for the MSSQL user.
- Database: The specific MSSQL database to connect to.
- Database URL: The MSSQL database connection URL (jdbc:// format).
Advanced Options:
- Trust Server Certificate: Toggle to enable trust for the server certificate (default is disabled).
- Encrypt: Toggle to enable or disable encryption for the connection (default is disabled).
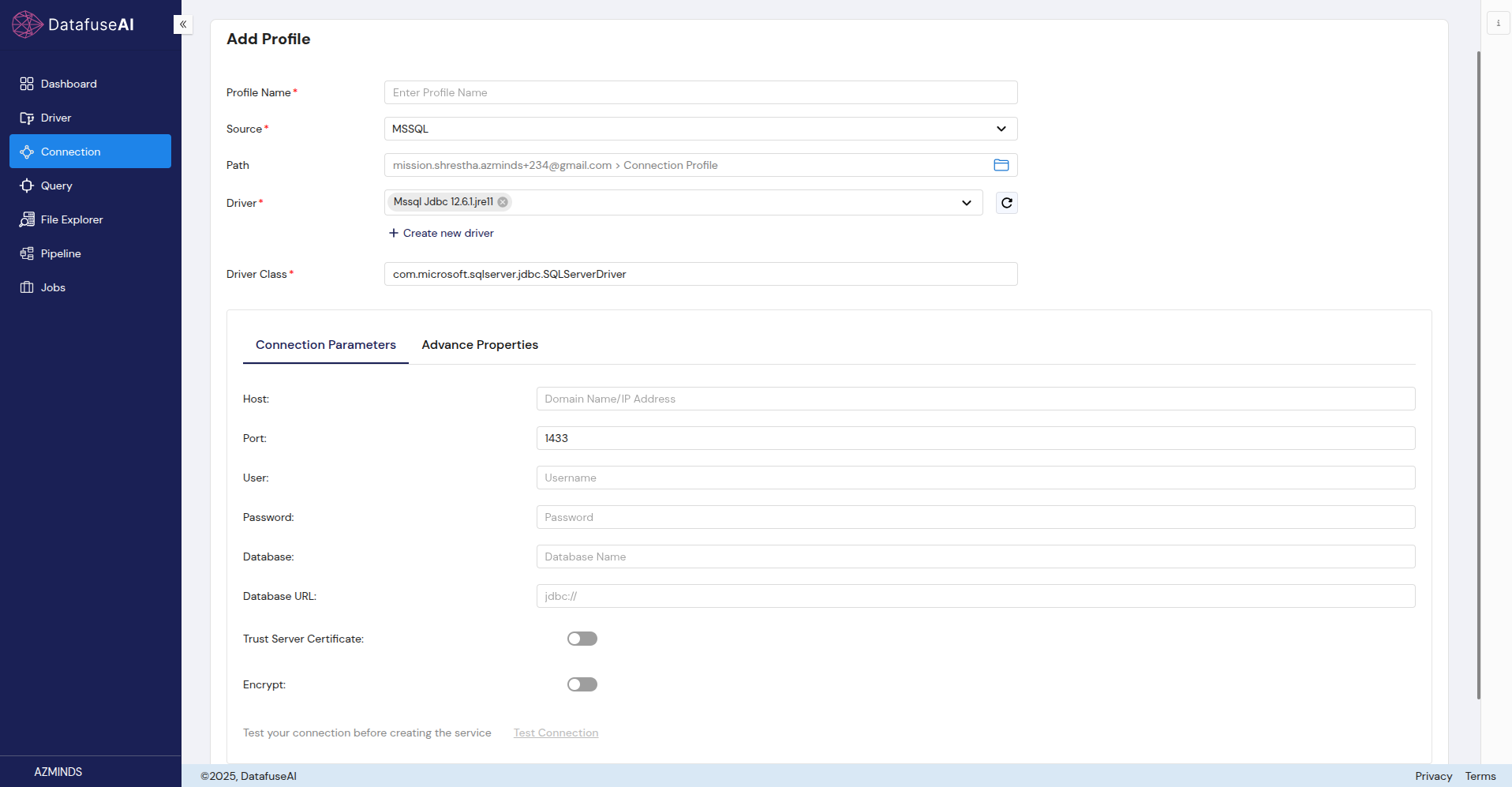
Snowflake
Snowflake is a cloud-based data warehousing service known for its scalability and integration with big data tools.
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: The name you assign to your Snowflake connection.
- Source: Select Snowflake from the data source options.
- Path: Displays the path for the Snowflake connection.
- Driver: Snowflake JDBC 3.13.30.
- Driver Class: net.snowflake.client.jdbc.SnowflakeDriver.
Connection Parameters:
- Host: The domain or IP address of the Snowflake instance.
- Port: The port used for Snowflake connections (443 is standard).
- User: Snowflake username.
- Authentication Type: Choose between Basic or SSO (Single Sign-On) authentication types.
- Password: Password for the Snowflake username.
- Database: The name of the Snowflake database.
- Schema: The schema within the database.
- Warehouse: The Snowflake warehouse to use.
2. NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases are used for large-scale data storage, particularly when dealing with semi-structured or unstructured data. Below is the setup for popular NoSQL databases.
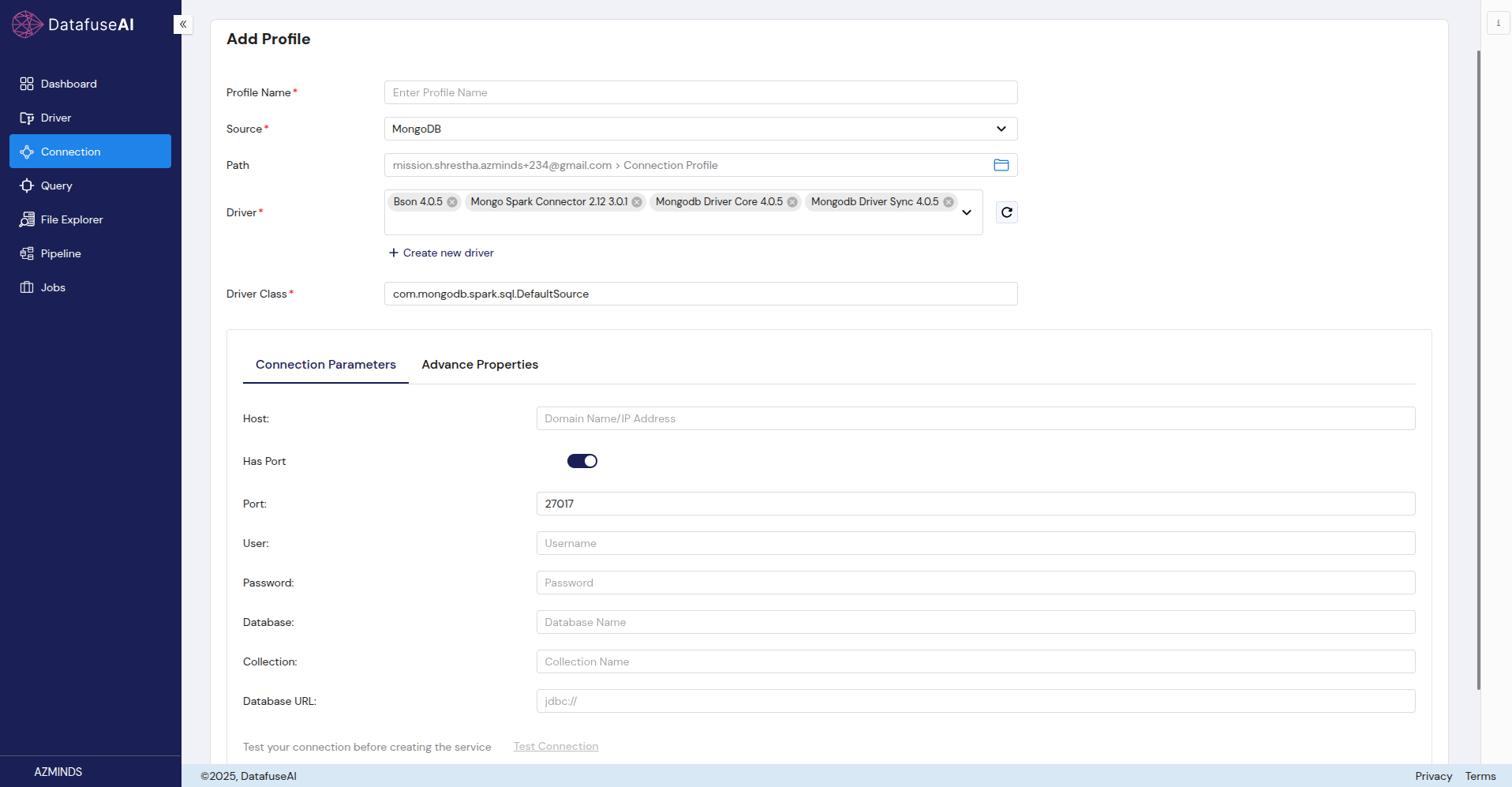
MongoDB
MongoDB is a widely-used NoSQL database that stores data in a flexible, JSON-like format.
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: Provide a name for the MongoDB connection profile.
- Source: Select MongoDB.
- Path: Displays the MongoDB connection path.
- Driver: Select Bson 4.0.5, Mongo, or MongoDriver.
- Driver Class: com.mongodb.spark.sql.DefaultSource.
Connection Parameters:
- Host: The domain name or IP address of the MongoDB server.
- Has Port: A checkbox to enable or disable port configuration (enabled by default).
- Port: The port number used by MongoDB (27017 is the default).
- User: The MongoDB username.
- Password: The MongoDB user password.
- Database: The MongoDB database you want to connect to.
- Collection: The collection within the MongoDB database.
- Database URL: The MongoDB database URL in jdbc:// format.
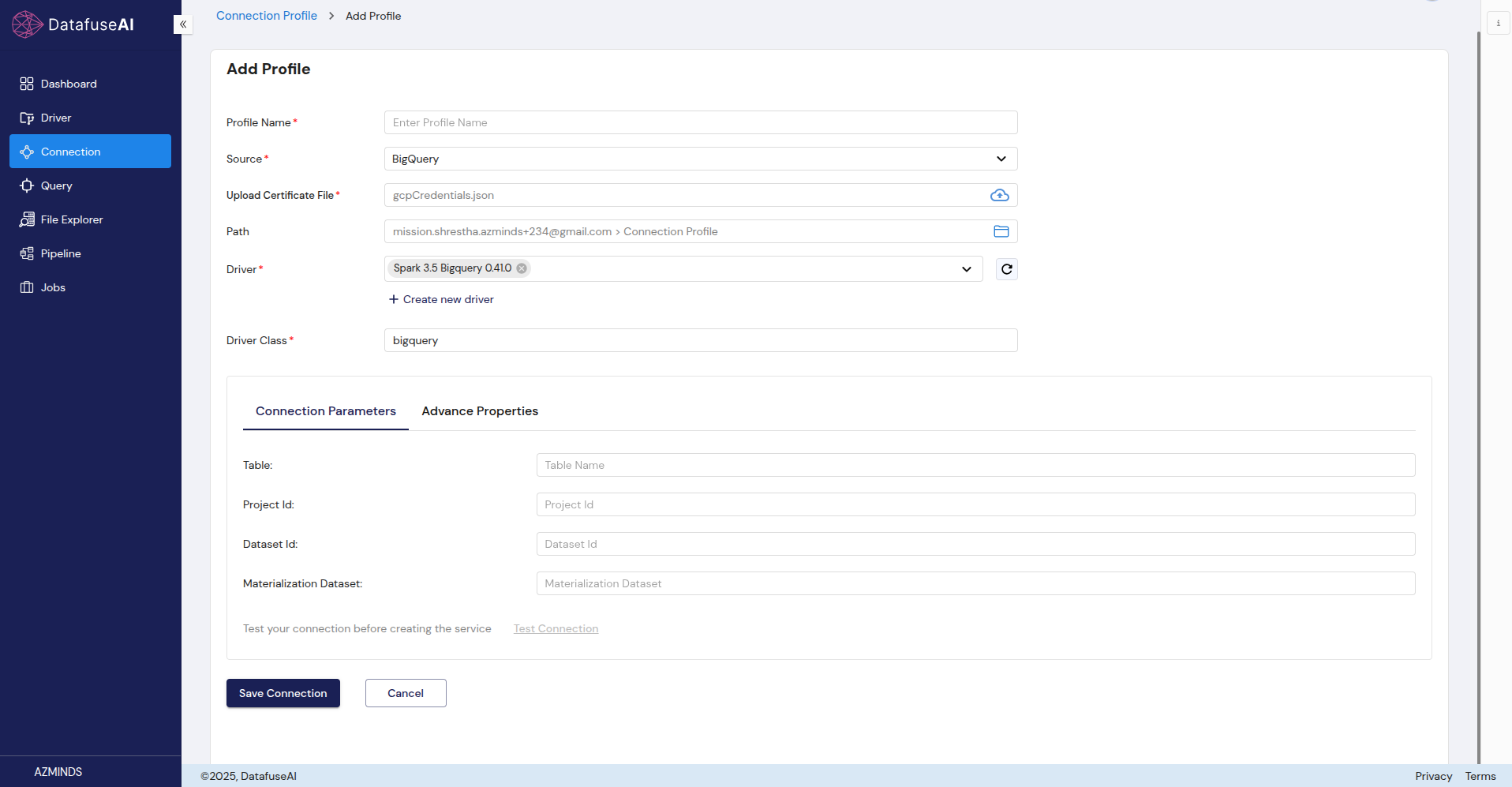
BigQuery
BigQuery is a fully-managed, serverless data warehouse from Google Cloud that allows real-time analytics on large datasets.
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: Name of the BigQuery connection profile.
- Source: Select BigQuery.
- Upload Certificate File: Upload your BigQuery connection certificate file.
- Path: The connection path for BigQuery.
- Driver: Select Spark 3.5 BigQuery O.4.10.
- Driver Class: bigquery.
Connection Parameters:
- Table: The BigQuery table that you wish to use.
- Project Id: The Google Cloud Project ID that houses the dataset.
- Dataset Id: The ID of the dataset in BigQuery.
- Materialization Dataset: The dataset to be used for materialization.
3. Cloud Storage & File Systems
Cloud storage systems such as Amazon S3, FTP, and SFTP allow for the storage of large volumes of data and provide easy access from multiple locations.
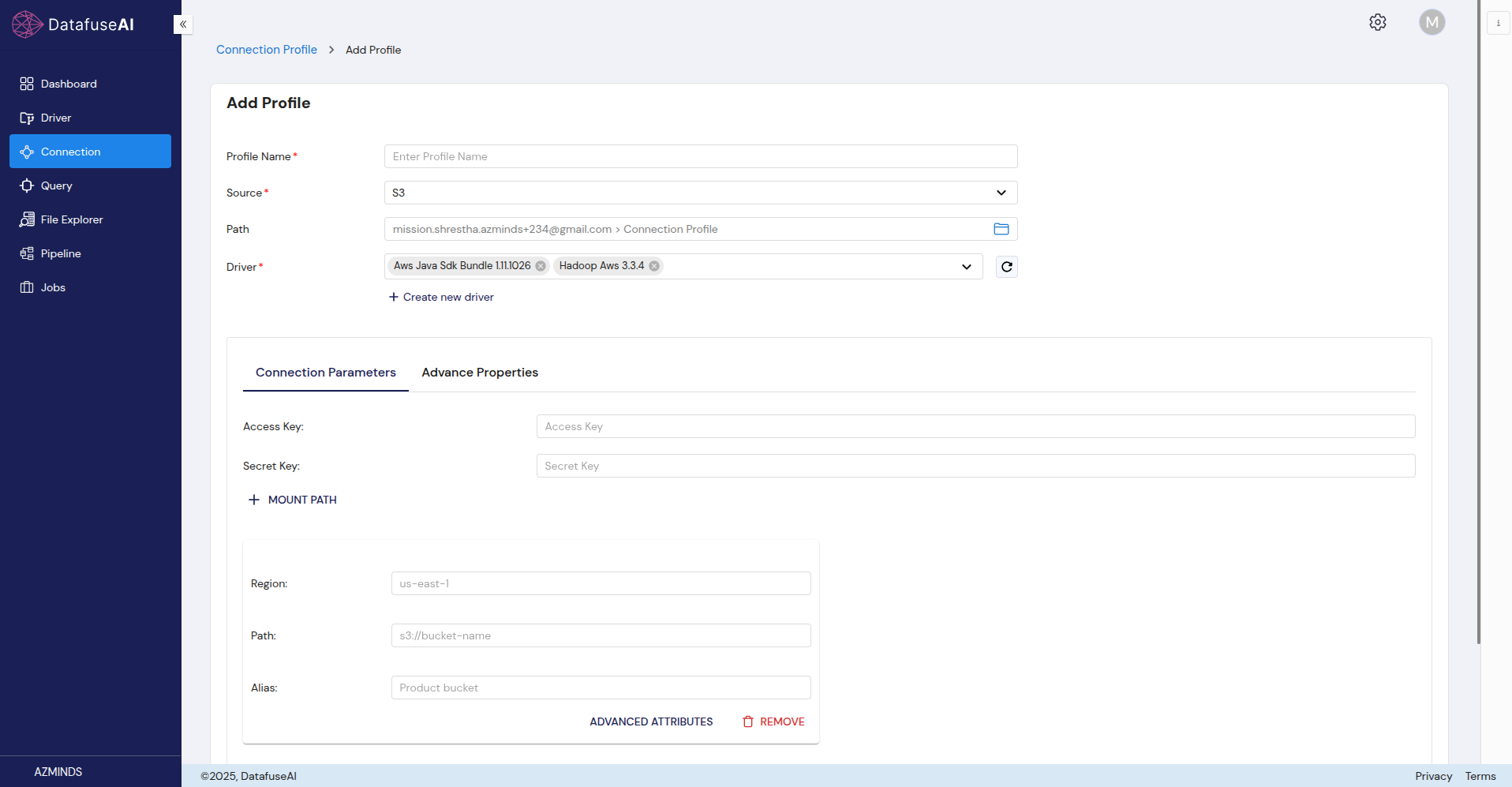
S3 (Amazon Simple Storage Service)
Amazon S3 is a cloud storage service widely used for storing and retrieving any amount of data.
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: Name for the S3 connection profile.
- Source: Select S3.
- Path: The S3 connection path.
- Driver: Choose the appropriate driver for S3.
Connection Parameters:
- Access Key: The key for authenticating your S3 connection.
- Secret Key: The secret key for the S3 connection.
- Region: The AWS region where the S3 bucket is located (e.g., us-east-1).
- Path: The path to the specific S3 bucket.
- Alias: A custom alias you can assign to the S3 bucket for easy reference.
Mount Path: Allows you to add additional sections for connecting to other regions, paths, or aliases.
FTP
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another over a TCP-based network.
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: Name of the FTP connection profile.
- Source: Select FTP.
- Path: Displays the FTP connection path.
Connection Parameters:
- Host: The domain name or IP address of the FTP server.
- Port: Default port (21) for FTP connections.
- User: Username for FTP authentication.
- Password: Password for the FTP user.
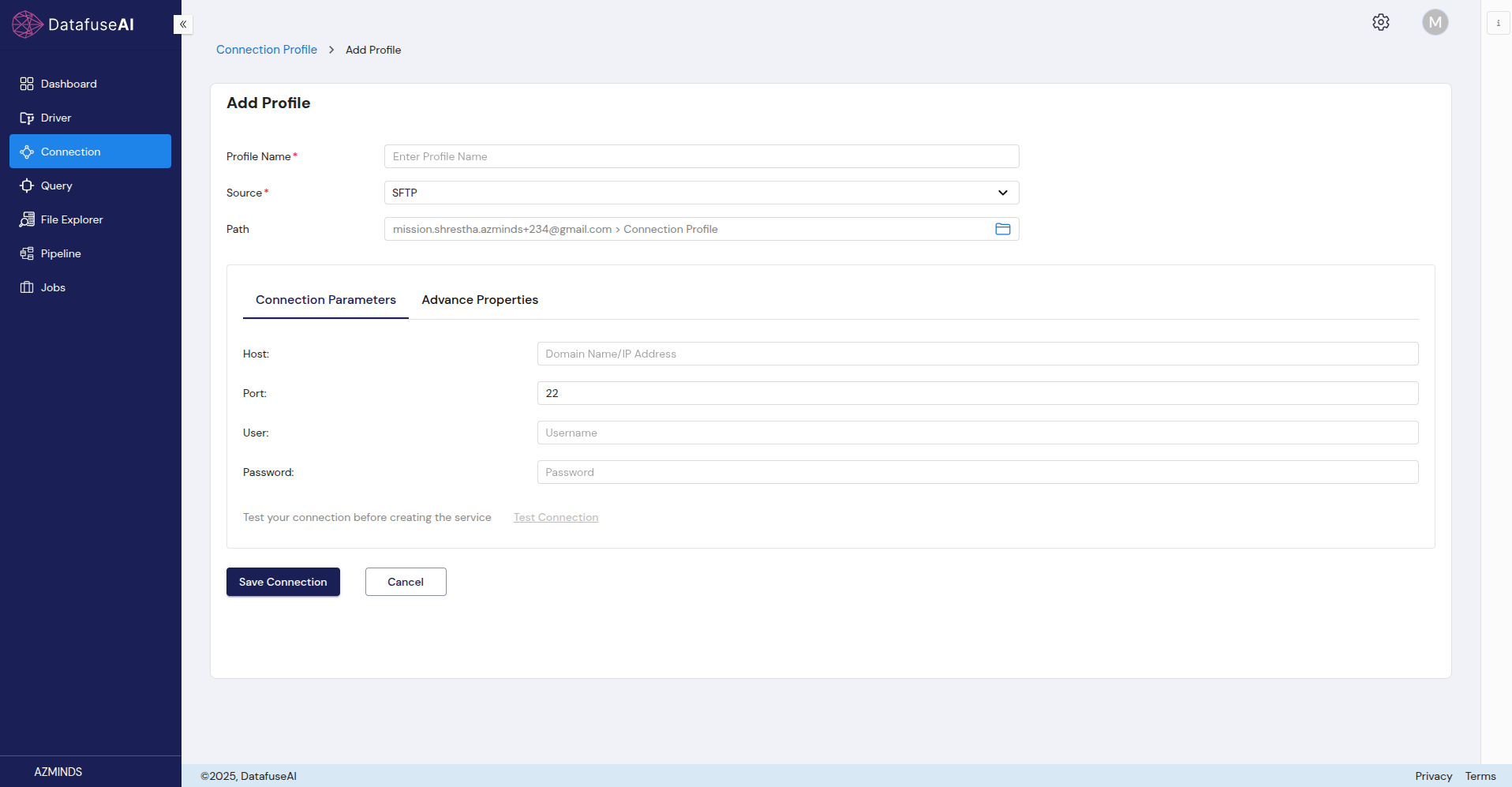
SFTP
SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) is a secure version of FTP that operates over SSH to ensure secure file transfers.
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: Name of the SFTP connection profile.
- Source: Select SFTP.
- Path: Displays the path for the SFTP connection.
Connection Parameters:
- Host: The domain name or IP address of the SFTP server.
- Port: Default port for SFTP connections (22).
- User: SFTP username.
- Password: Password for the SFTP user.
4. Cloud Databases and RDS
Cloud-based databases such as RDS MariaDB, RDS MySQL, and Azure PostgreSQL offer managed database services with automatic backups and scaling.
RDS MariaDB
RDS MariaDB is a managed relational database service based on MariaDB provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: Name of the RDS MariaDB connection profile.
- Source: Select RDS MariaDB.
- Path: Displays the RDS MariaDB connection path.
- Driver: "MariaDB JDBC 2.7.3".
- Driver Class: org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver.
Connection Parameters:
- Host: The domain name or IP address of the RDS MariaDB instance.
- Port: Default MariaDB port (3306).
- User: MariaDB username for authentication.
- Password: Password for the MariaDB user.
- Database: The MariaDB database you wish to connect to.
- Database URL: URL for the RDS MariaDB database (e.g., jdbc://).
RDS MySQL
RDS MySQL is a managed database service based on MySQL provided by AWS.
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: Name of the RDS MySQL connection profile.
- Source: Select RDS MySQL.
- Path: Displays the path for the RDS MySQL connection profile.
- Driver: "MySQL JDBC Driver".
- Driver Class: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver.
Connection Parameters:
- Host: Domain or IP address of the RDS MySQL instance.
- Port: The port to connect to (3306).
- User: RDS MySQL username for authentication.
- Password: Password for the RDS MySQL user.
- Database: The name of the RDS MySQL database.
- Database URL: URL for RDS MySQL database (e.g., jdbc://).
Azure PostgreSQL
Azure PostgreSQL is a managed PostgreSQL database service provided by Microsoft Azure.
Form Fields:
- Profile Name: Name of the Azure PostgreSQL connection profile.
- Source: Select Azure PostgreSQL.
- Path: Displays the path for the Azure PostgreSQL connection profile.
- Driver: "Postgresql JDBC 42.2".
- Driver Class: org.postgresql.Driver.
Connection Parameters:
- Host: The domain name or IP address of the Azure PostgreSQL server.
- Port: Default PostgreSQL port (5432).
- User: Azure PostgreSQL username.
- Password: Password for the Azure PostgreSQL user.
- Database: Name of the Azure PostgreSQL database.
- Database URL: URL for Azure PostgreSQL database (e.g., jdbc://).
Troubleshooting and Support
Common Issues
Issue 1: Test Connection Fails (Red Indicator)
-
Cause: Incorrect password, wrong IP address, or the database is behind a firewall.
-
Solution:
- Check for typos in the "Host" and "Password" fields.
- Ensure the "Port" number matches your database settings.
- Ask your IT team if the DataFuse AI IP address is allowed through the firewall.
Issue 2: Unable to Delete a Profile
- Cause: The profile is currently being used in a Pipeline or Query.
- Solution: Click the Uses button to see where it is active. Remove the profile from those pipelines first, then try deleting again.
Issue 3: "Driver Not Found" Error
- Cause: The selected Driver does not match the Source.
- Solution: In the Edit screen, ensure the Driver dropdown matches your Source (e.g., select Postgresql 427.3 for a PostgreSQL source).
Conclusion
This guide offers a comprehensive breakdown of Connection Profile Management in DataFuse AI. It covers the complete process of creating, managing, and testing Connection Profiles for various data sources, both relational and NoSQL databases, cloud storage, and RDS instances. By following the steps outlined, users can ensure secure and efficient data integration into DataFuse AI.